In this article, we have discussed formulas of important 2D figures which are frequently asked. We have compiled important information which are mostly asked in SSC Exams at one place.
# Rectangle

Let d1 and d2 are diagonals of the given rectangle ABCD.
then, both diagonals are equal but not perpendicular to each other.
# Path outside the rectangle
Suppose there is a park having length l and breadth b. There is a road of width x outside of it.

Then, Area of path = 2x (l + b + 2x)
# Path inside the rectangle
Suppose there is a park having length l and breadth b. There is a road of width x inside of it.

Then, Area of path = 2x (l + b – 2x)
# When there is a road along both the length and breadth of the park.

Then, Remaining area of Rectangle (shaded region) = (l–x) (b-x)
Area of the path = lx + bx – x2
Area of the path = lx + bx – x2
# Circle: Given a circle of radius ‘r’

We recommend you learn this table as it will save your time in calculating these all.
If radius is ‘r’, then perimeter = 2πr and Area = πr2
Radius
|
Perimeter (2πr)
|
Area (πr2)
|
7
|
44
|
154
|
14
|
88
|
616
|
21
|
132
|
1386
|
28
|
176
|
2464
|
35
|
220
|
3850
|
42
|
264
|
5544
|
# Length of Rope
Let ‘d’ is the diameter of pulley and ‘r’ is the radius, then d = 2r. All pulleys are similar.
Let ‘d’ is the diameter of pulley and ‘r’ is the radius, then d = 2r. All pulleys are similar.

Length of rope = 2d + 2pr

Length of rope = 3d + 2pr

Length of rope = 4d + 2pr
Note: Trick to remember these formulas: number of pulleys x diameter + Perimeter of one pulley
#Sector
In this circle, ‘r’ is the radius, θ is the angle made by the arc of length ‘l’
 |
Length of arc
Area of sector
Area of sector when ‘l’ is given
|
# Segment

Area of minor segment 
Area of major segment 
# Area of shaded portion





# Inradius and Circumradius of Square:
There is a square of side ‘a’; ‘r’ is the inradius and ‘R’ is the circumradius.
 |  |
# Triangle:
Let ABC is a triangle and M1, M2 and M3 are medians of the given triangle.

Then, 

# Inradius of triangle:
Given, ABC is a triangle and a, b and c are the sides of given triangle. Let ‘r’ is the inradius of triangle.

# Circumradius of triangle:
Given, ABC is a triangle and a, b and c are the sides of given triangle. Let ‘R’ is the circumradius of triangle.

# Right angle triangle
Given ‘a’ is the base, ‘b’ is the perpendicular and ‘c’ is the hypotenuse of triangle ABC.


# Equilateral triangle:




Where, h is the height of triangle, 
Hence, we can say that height of equilateral triangle is equal to the sum of side perpendicular of the triangle.
# Isosceles triangle

# Regular Polygon
Let, n = no. of sides of regular polygon and a = length of side of regular polygon
# Internal angle of regular polygon = 
# Sum of internal angle of regular polygon 
# Angle made by centre = 
#Area of Regular polygon 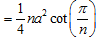
# External angle of regular polygon 
# sum of all external angle = 360º
# sum of all external angle = 360º
# For Regular Hexagon
 |
Circumradius R = a
Inradius
|
# Cyclic Quadrilateral

# Parallelogram
Let a and b are the sides, h is the height and d1 and d2 are the diagonals of parallelogram

then,
Area of parallelogram = (i) Base × height
(ii) 
(iii) 
Imp. Relation 
Imp. Note: In rectangle, parallelogram, square and Rhombus diagonals bisect other.
# Rhombus
 |
In Rhombus, diagonals are not equal to each other but they bisect each other at 90 degree.
Area = Base × height = a x h
Or Area 
# Trapezium

Case 1: If AD = BC, then DM = CN
# Quadrilateral

Comments
Post a Comment